Key Stage 3 (often abbreviated to KS3) is the legal wording for the first three years of secondary school education in English and Welsh maintained schools. The years KS3 covers are Years 7, 8 and 9. Pupils usually start Key Stage 3 at the age of 11 and complete it according to the national curriculum 3 years later when they have turned/or are about to turn 14.
What is on the Key Stage 3 curriculum?
Core Subjects in Key Stage 3:
The compulsory subject areas covered on the national curriculum in Key Stage 3 include the core subjects: English, Maths, Science, and Modern Foreign Languages (MFL).
Additional Subjects:
In addition to the core subjects, pupils at Key Stage 3 must choose at least one subject from the following options: Art & Design, Design & Technology, Music, Geography, History, Computing, and PE.
Citizenship & Relationship Education
Alongside the core subjects, students also engage in Citizenship and Relationship and Sex Education (RSE). Citizenship education aims to develop students’ understanding of their rights, responsibilities, and the democratic processes within society. It covers topics such as government, law, and human rights.
RSE, on the other hand, focuses on fostering healthy relationships and equipping students with the knowledge and skills needed to navigate friendships, family dynamics, and respectful interactions. It covers aspects such as consent, diversity, and emotional well-being. Both subjects are essential in helping students develop a strong sense of identity, empathy, and an understanding of their place in the world.
It’s worth noting that maintained schools are required to teach RSE, However, parents/carers have the right to remove their children from these lessons without explanation.
How are assessments from Key Stage 3 used?
Achievement levels at KS3 will have an impact on what students are able to choose at the ‘Options‘ stage, when they select the subjects they’d like to study at Key Stage 4 for GCSE level.
What happens at the end of Key Stage 3?
At the end of this stage, teachers create a skills assessment for each pupil. Most schools use course work completed throughout Year 9 to do this though some schools also test pupils. The national standard that students are expected to achieve by the end of KS3 is between 5 and 6. Their assessments are therefore compared to this level to indicate whether they have or have not reached this expected standard.
Transition to Key Stage 4
The transition from Key Stage 3 to Key Stage 4 marks an important milestone in a student’s educational journey. As they progress from earlier key stages, the focus shifts towards a wider understanding of subjects and a more specialized approach to their studies. Key Stage 4, commonly known as secondary education, lays the foundation for future academic and vocational pursuits. Students are introduced to a broader range of subjects within the curriculum, allowing them to explore their interests and potential career paths. While core subjects such as English, Maths, and Science continue to be taught, students also have the opportunity to delve deeper into areas such as humanities, arts, and languages. This phase of education sets the stage for the upcoming challenges, usually culminating in the pursuit of GCSEs (General Certificate of Secondary Education) or equivalent qualifications, equipping students with vital knowledge and skills for various aspects of life beyond school.
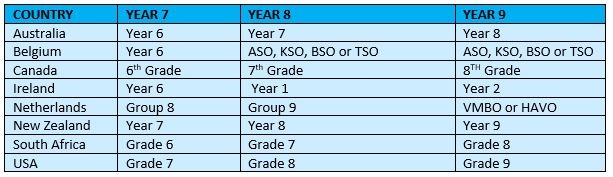
What are the overseas equivalents of Key Stage 3?
While Key Stage 3 is specific to the educational system in England and Wales, there are overseas equivalents that align with the concept of secondary school education. In many countries, secondary education follows a similar structure, providing a foundation for students to progress academically. The national curriculum taught during this stage may vary, but the core subjects of math and literacy tend to be emphasized universally. Additionally, countries may have their own national qualifications or assessments that students work towards, equivalent to the English system’s GCSEs. Some countries also have their own versions of an English baccalaureate, which recognizes achievement in key subject areas. Overall, the aim of these overseas equivalents is to provide students with a well-rounded education, covering essential knowledge and skills in the following areas to prepare them for further studies or the workforce.
You can find information about Key Stage 1 here, Key Stage 2 here and Key Stage 4 here.
You can find our teaching jobs in the UK secondary schools here. UK based teachers and teaching assistants can pre-register with us here and overseas ones here.
Teaching Blog
No results found.....